
Digital PCR/Quantitative PCR Service
Digital PCR (dPCR) is a method for absolute quantification of nucleic acids. Unlike qPCR, dPCR does not rely on standard curves. The sample is partitioned into many individual chambers (8.5K or 2.6K) in a microfluidic chip. After partitioning, the reactions undergo end-point PCR cycling, and partitions are analyzed for the presence or absence of a fluorescent signal. The number of nucleic acid molecules is then calculated based on the principles of Poisson distribution. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) is a technique used to quantify specific DNA or RNA molecules present in a sample. It employs fluorescent dyes or probes to monitor the amplification products in real-time during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process, enabling quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids. This technique is widely used in fields such as gene expression analysis, virus detection, genotyping, and copy number variation analysis.
Digital PCR (dPCR) Service
Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Service
Digital PCR (dPCR) Service
Digital PCR (dPCR) is a method for absolute quantification of nucleic acids. Unlike qPCR, dPCR does not rely on standard curves. The sample is partitioned into many individual chambers (8.5K or 2.6K) in a microfluidic chip. After partitioning, the reactions undergo end-point PCR cycling, and partitions are analyzed for the presence or absence of a fluorescent signal. The number of nucleic acid molecules is then calculated based on the principles of Poisson distribution. dPCR has a lower detection limit and higher precision than qPCR.
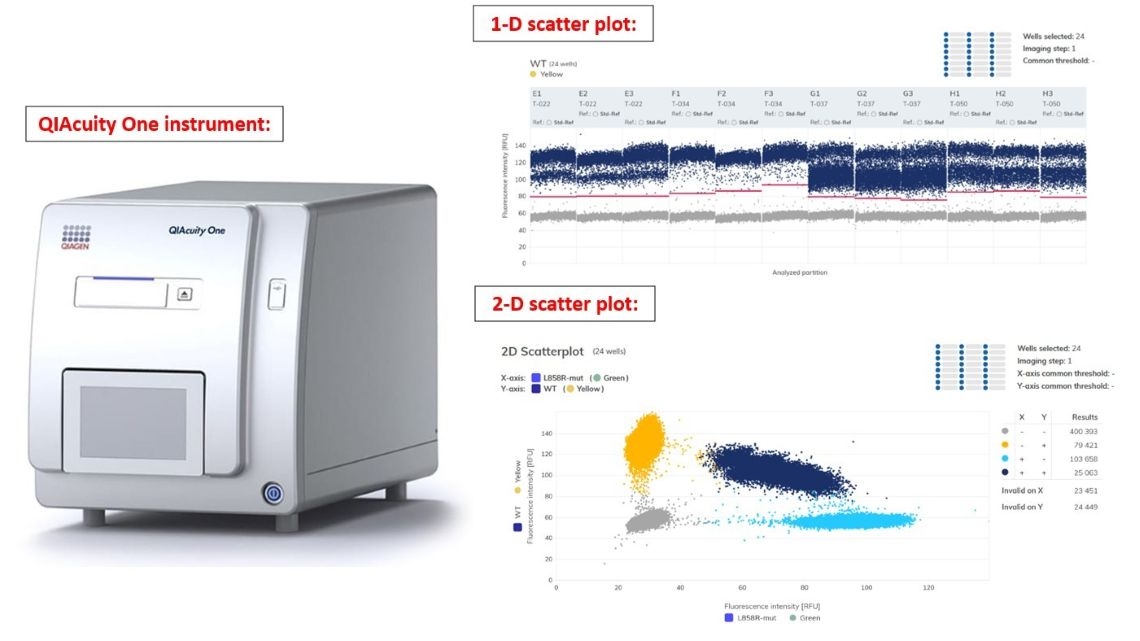
🌟 Instrument: QIAcuity One instrument (Qiagen)
🌟 EvaGreen or TaqMan Probe system can be chosen to use.
🌟 Application:
(1) Mutation detection.
(2) Probiotics or pathogen detection.
(3) Copy number variation analysis.
(4) miRNA research.
(5) Quantification of NGS libraries.
🌟 The instrument allows selection of an 8-well or 24-well plate (Nanoplate) based on the number of samples. The reaction volume is 40 µl.
Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Service
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) is a technique used to quantify specific DNA or RNA molecules present in a sample. It employs fluorescent dyes or probes to monitor the amplification products in real-time during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process, enabling quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids. This technique is widely used in fields such as gene expression analysis, virus detection, genotyping, and copy number variation analysis.
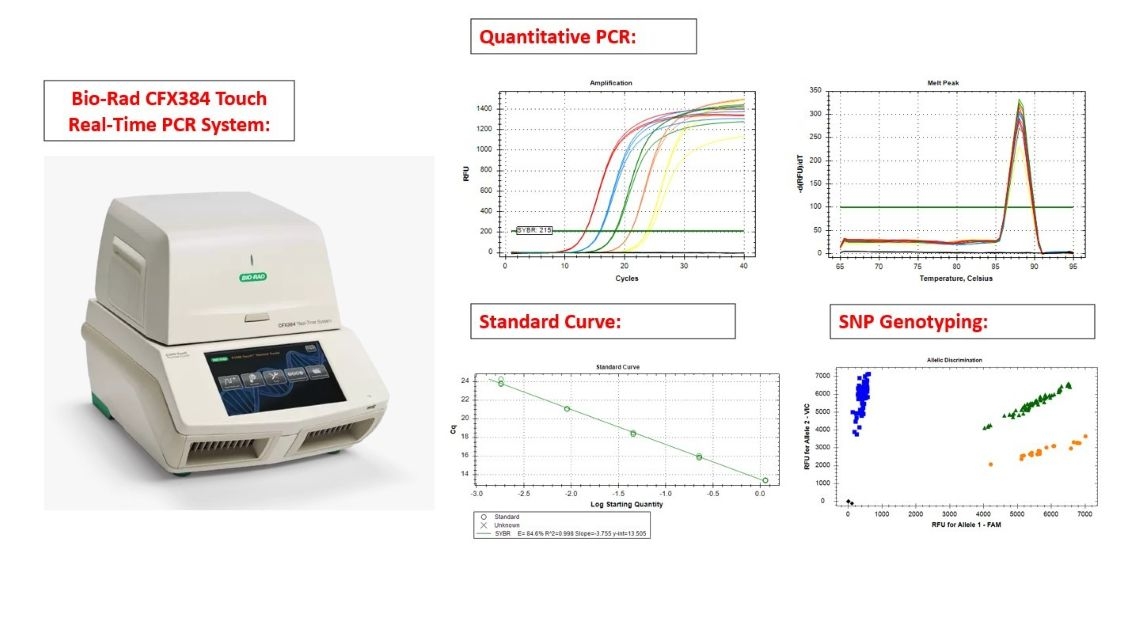
🌟 Instrument: CFX384 Touch Real-Time PCR System (Bio-Rad)
🌟 Instrument: CFX384 Touch Real-Time PCR System (Bio-Rad)
🌟 Accepted sample formats:
(1) Cell pellet or tissue samples.
(2) RNA.
(3) cDNA or DNA.
🌟 Application:
(1) Gene Expression Analysis: Using SYBR Green or TaqMan Probe systems.
(2) Standard Curve Construction: Using SYBR Green or TaqMan Probe systems.
(3) SNP(Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) Assay: Using TaqMan Probe system.
🌟 The 384-well plate is used. The minimum reaction volume for quantitative analysis is 10 µl, while for SNP assay, the minimum reaction volume is 5 µl.
Strain Identification
Advantages of Strain Identification Service :
1. Genetic identification methods analyze bacterial 16S and fungal ITS, capable of identifying at the "species" level.
2. Both agar plates and liquid cultures of individual strains are applicable. Genomic DNA of microorganisms can also be submitted for identification.
3. Reports are generated within 5 working days upon sample receipt.
4. A dedicated data management system is available for customers to download files.